Abstract
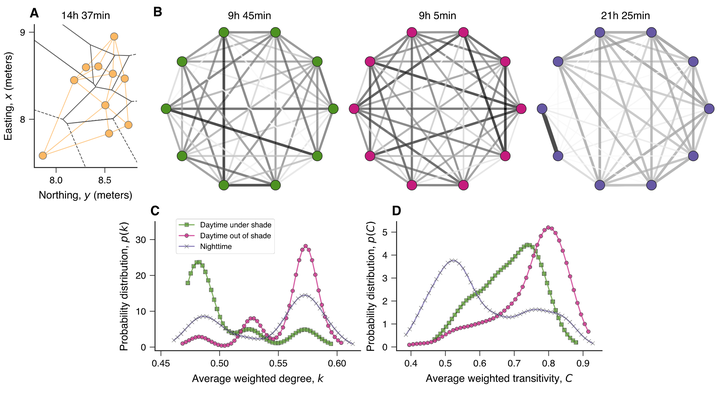
Despite significant efforts devoted to understanding the underlying complexity and emergence of collective movement in animal groups, the role of different external settings on this type of movement remains largely unexplored. Here, by combining time series analysis and complex network tools, we present an extensive investigation of the effects of shady environments on the behavior of a fish species (Silver Carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) within earthen ponds. We find that shade encourages fish residence during daylight hours, but the degree of preference for shade varies substantially among trials and ponds. Silver Carp are much slower and exhibit lower persistence in their speeds when under shade than out of it during daytime and nighttime, with fish displaying the highest persistence degree and speeds at night. Furthermore, our research shows that shade affects fish schooling behavior by reducing their polarization, number of interactions among individuals, and the stability among local neighbors; however, fish keep a higher local degree of order when under shade compared to nighttime positions.