Identifying and modeling patterns oftetrapod vertebrate mortality rates in the Gulf of Mexico oil spill
Abstract
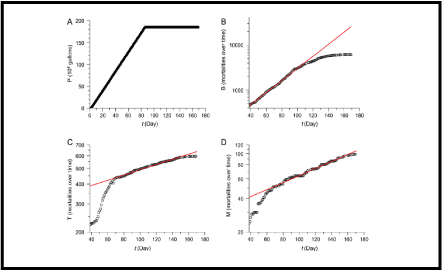
The accidental oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010 has caused perceptible damage to marine and freshwater ecosystems. The large quantity of oil leaking at a constant rate and the long duration of the event caused an exponentially increasing mortality of vertebrates. Using data provided by NOAA and USFWS, we assessed the effects of this event on birds, sea turtles, and mammals. Mortality rates (measured as the number of carcasses recorded per day) were exponential for all three groups. Birds were the most affected group, as indicated by the steepest increase of mortality rates over time. For sea turtles and mammals, an exponential increase in mortality was observed after an initial delay. These exponential behaviors are consistent with a unified scenario for the mortality rate for tetrapod vertebrates. However, at least for mammals, pre-spill data seem to indicate that the growth in the mortality rate is not entirely a consequence of the spill.