Abstract
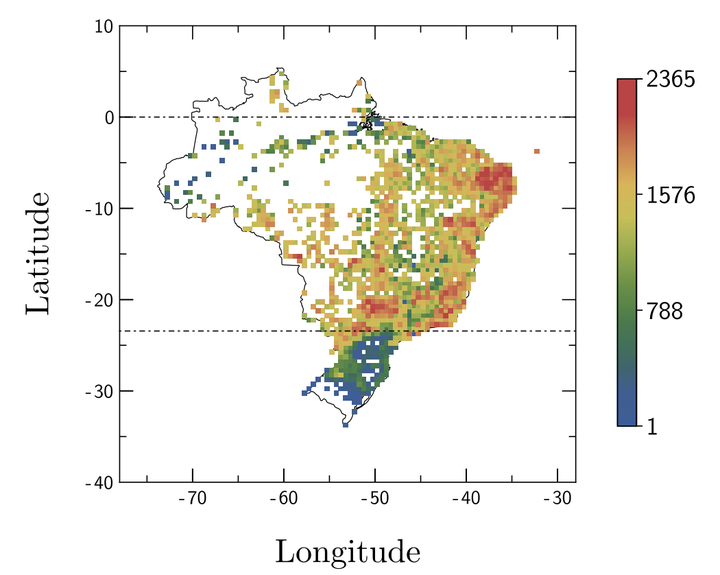
Dengue infection plays a central role in our society, since it is the most prevalent vector-borne viral disease affecting humans. We statistically investigated patterns concerning the spatial spreading of dengue epidemics in Brazil, as well as their temporal evolution in all Brazilian municipalities for a period of 12 years. We showed that the distributions of cases in municipalities follow power laws persistent in time and that the infection scales linearly with the population of the municipalities. We also found that the average number of dengue cases does not have a clear dependence on the longitudinal position of municipalities. On the other hand, we found that the average distribution of cases varies with the latitudinal position of municipalities, displaying an almost constant growth from high latitudes until reaching the Tropic of Capricorn leveling to a plateau closer to the Equator. We also characterized the spatial correlation of the number of dengue cases between pairs of municipalities, where our results showed that the spatial correlation function decays with the increase of distance between municipalities, following a power-law with an exponential cut-off. This regime leads to a typical dengue traveling distance. Finally, we considered modeling this last behaviour within the framework of a Edwards-Wilkinson equation with a fractional derivative on space.